Did you know that about one-fifth of sent emails go to spam or aren’t delivered at all?
This might not sound like a lot, but if your goal is to generate revenue through emails, then you’re losing out on profits you could’ve earned!
Our team has carried out extensive research on email deliverability and the aspects that affect it. We concluded that deliverability success is directly influenced by domain health (DNS settings are accountable for 50% of your deliverability success) and sender reputation. In turn, sender reputation relies on the reply rate. In simple terms, sending a high volume of emails and having a minimal response rate (say, 1-2% or none at all) can negatively impact sender reputation.
To help you understand the ins and outs of this complex topic, we have created a comprehensive guide on email sending process, how to take care of sender reputation, and what you can do to get your emails right into your contact’s inbox.
The guide covers many issues and includes a lot of terms. So, for your convenience, we’ve outlined its main chapters. If you are here for the email deliverability audit and best practices only—feel free to skip the basics.
We’ve also created a glossary of terms you can find below the post. Get back to any of them whenever you need!
Now off we go!
Outline:
What is email deliverability?
|
Email deliverability (inbox placement) is the percentage of emails you’ve successfully delivered to your subscribers’ inboxes. Its key objective is to get your message not simply delivered but placed right into the recipient’s primary tab. |
That’s what differs email deliverability from the delivery rate, which counts all emails as delivered if they didn’t bounce (yes, those landing in the spam folder, too!).

Why should I care about email deliverability?
Good email deliverability is critical to your email marketing strategy, and here’s why:
- You ensure your messages fly right into the inbox, avoiding the spam folder, where they are destined to rest in peace.
- The more emails find their way into your customer’s primary tab, the higher chances they will be read. Is this not the main gist of your email outreach campaigns?
- You get a competitive advantage as you will have more chances to be visible among the mickle of messages your recipients get every day, unlike those of your competitors who neglect improving their email deliverability.
- Sending more emails to the customer’s inbox, getting them opened and read, and engaging your subscribers with your content is a sure way to boost the effectiveness of your email marketing campaigns, improving your ROI.
To figure out how to boost your email deliverability, you need to understand the whole email sending process. Figuratively speaking, you need to know how your email travels from the departure to the destination point.
|
Improve your engagement, bounce rate and email placement with Snov.io Email Deliverability Month 🔥 Join for free and get daily bite-sized lessons right in your inbox! |
How the email sending process works
Say, you’ve just created an email to inform your subscribers about your new loyalty program. You’ve built and segmented your email list, and now you’re just about to press the “Send” button. Let’s see what follows step by step.
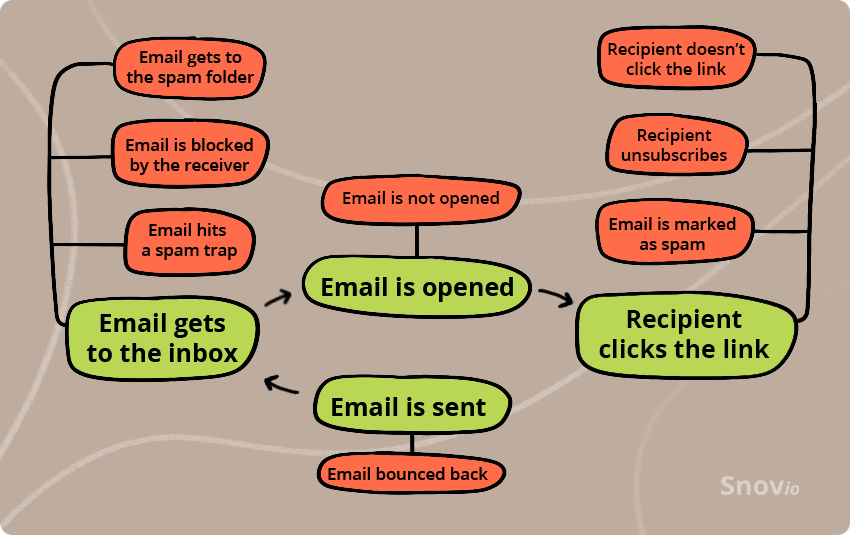
Step 1. Your email is sent
Once you’ve pressed the “Send” button, there are two possible scenarios:
1.1. Your email is delivered
In this scenario, your message is delivered to the recipient successfully.
1.2. Your email bounced back
|
A bounce means a mail server has rejected your message. When this happens, you typically receive an automatic delivery failure notification. |
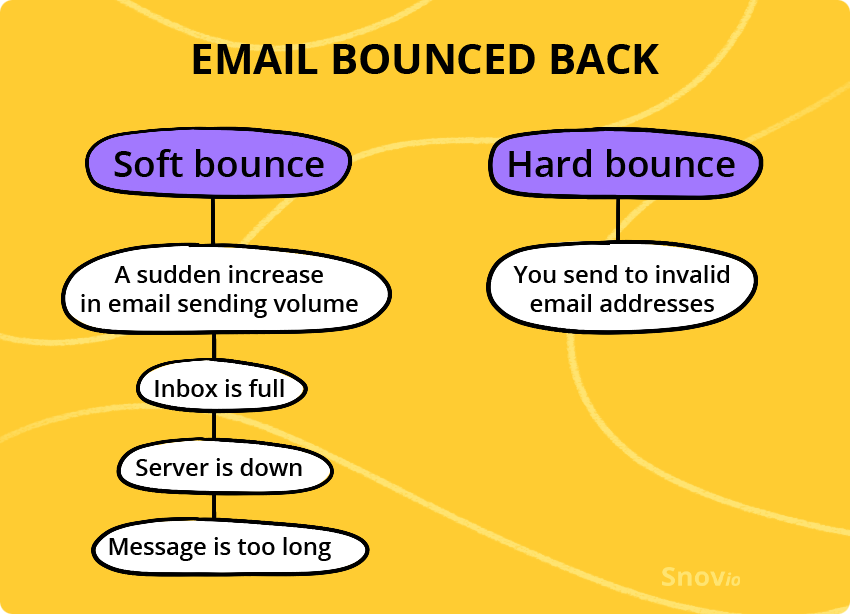
There are two types of bounces you might get: a soft or a hard bounce:
- A soft bounce happens to your email due to several reasons: there’s a sudden increase in email sending volume, the recipient’s inbox is full, the server is down, or the email size is too large. For instance, if you usually send 1K emails a day, but then increase the volume to 7K, those extra 6K emails might soft-bounce.
- A hard bounce occurs when you send an email to an invalid address, i.e., the address that doesn’t exist.
The biggest problem about hard bounces is that by having lots of them, you risk being treated as a fraudulent email sender. This is why it’s better to verify your email lists before sending out your campaigns.
Email verification is not a difficult task when you have a reliable tool to help you. With Snov.io, you may quickly verify email addresses for free.
Step 2. Your email is delivered/not delivered
Whether your email gets to the recipient’s inbox is controlled by email sending gateways, such as ISPs or blacklisting organizations.
|
ISPs (Internet Server Providers) provide mailboxes to end-users as a part of their paid services. In email marketing, ISPs refer to major inbox providers such as Gmail, Outlook, Yahoo, or Inbox by Gmail. |
They protect their customers from receiving unsolicited emails by:
- Establishing sending limits
- Blocking suspicious senders
- Default sending email to the junk or spam folder
- Blacklisting.
|
Blacklisting organizations are companies that provide blacklists containing senders who, they consider, are following fraudulent email sending practices. As a rule, ISPs use these reports to monitor and control email sending. |
2.1. Your email gets to the inbox
Now all that’s left for you is just waiting for your email to be opened and read.
But as we’ve already mentioned, 1 in 5 emails go to a spam folder, hit a spam trap, or get blocked by the receiver. Let’s discuss these unlucky cases.
2.2. Your email gets to the spam folder
|
Spam (aka junk email) is unsolicited emails sent in bulk to people who haven’t given consent to receiving them. |
Whether your email gets to the spam folder is a matter of several factors — the number of emails you’ve sent before, the number of emails you are trying to send right now, and where you are sending them from.
Read more about the reasons your emails may find themselves in the spam folder and what you can do about it in one of our previous blog posts.
2.3. Your email is blocked by the receiver
The receiving server may temporarily reject your email, and here’s why:
- You’re sending content that looks spammy (excessive use of CAPS, punctuation, promotional language, or spam trigger vocabulary).
- You’ve got too many complaints.
- You’ve been sending emails to invalid addresses.
This points to the necessity of working on your email copy and practicing healthy email sending behavior.
2.4. Your email hits a spam trap
|
A spam trap is an invalid email address used by ISPs or blacklist operators to identify senders who are neglecting best email practices or an email address that was once valid but now is abandoned or not legitimate. |
There are two spam trap types:
- A pristine spam trap is an email address that has never been valid. It’s used to spot senders with bad list-building behavior like purchasing email lists or scraping emails from websites without verification.
- A recycled spam trap is an email address that was once valid but was then abandoned and further turned into a spam trap.
To avoid spam traps, don’t purchase email lists, use scraping software with pre-verification features (Snov.io is one of such tools), and clean your email lists regularly.
Step 3. Your email is opened/not opened
Open rate is one of the most important email performance metrics to track. If you want to know more about what a good email open rate is, how to calculate it, and how to improve it, check out one of our posts.
And as for email tracking, you may get the help of special tools that track email opens right in your Gmail account for free.
Step 4. The recipient interacts with your email
What is your customer going to do next? They may read your email and click through, close it without clicking the link, mark it as spam, or unsubscribe from your emails.
4.1. The recipient clicks the link
That’s basically what you want your customers to do with your email. If they click on something, it will tell you your content keeps your recipients engaged.
4.2. The recipient doesn’t click the link
Unlike the first scenario, if your email isn’t clicked through, it signifies you should work more on improving engagement. Yet, it’s not critical for the ISPs.
4.3. The recipient unsubscribes
This means you’ve lost contact with subscribers. But don’t be sad about it!
People tend to unsubscribe, the average unsubscribe rate being 0,17%. That’s inevitable, and you should let people leave you (still measuring unsubscribe rate and analyzing how to improve engagement).
Another good news is that unsubscriptions won’t cast a shadow on your reputation!
4.3. The recipient marks your email as spam
This will harm your reputation, though. Prospects may mark your emails as spam due to several reasons: say, it’s difficult to unsubscribe from your campaigns, or you are sending irrelevant content. You should respect your subscribers and give them what they want, including an easy option to unsubscribe from your messages.
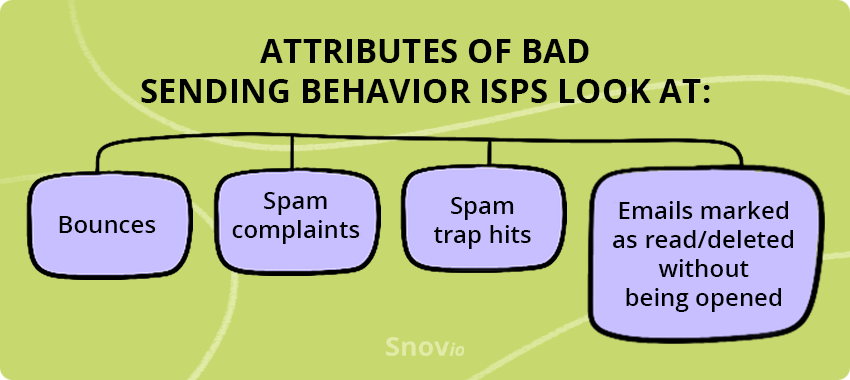
Remember, you need to prove to ISPs you are a good sender; otherwise, your sender reputation can be in danger.
Let’s talk about it in detail.
Sender reputation — a key component of your email deliverability
Sender reputation has a direct influence on whether your emails will find their place in your customer’s inbox. That’s why we decided to dedicate a separate chapter to it.
What is sender reputation?
|
Sender reputation is the method used by mailbox providers to measure how trustworthy your sender’s email is. In simple words, this is your status as a sender that depends on many factors, including content quality, the quality of your contacts, recipient engagement, and so on. |
Sender reputation has three components: IP reputation, domain reputation, and content reputation.
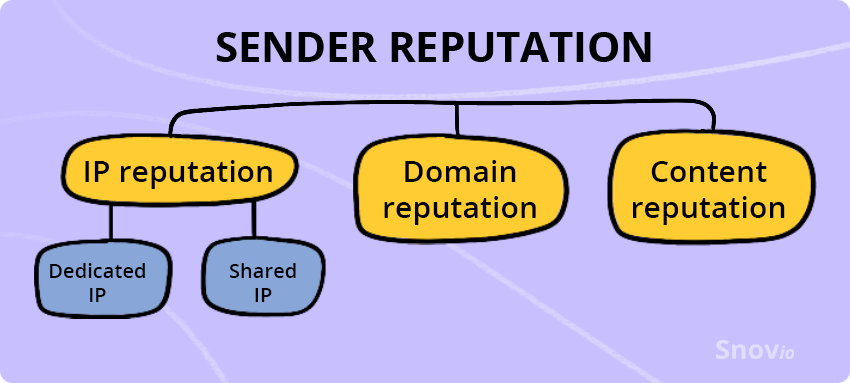
IP reputation is the reputation of the IP address your email comes from no matter what company you represent.
Every computer or server has a unique identifying address called IP address. So, if you send emails from a specific computer or server, you tie yourself with a specific IP. It allows ISPs to track your IP reputation.
As an email sender, you may either have a dedicated or a shared IP address.
- A dedicated IP address is your IP address, the one you don’t share with anyone else. With a dedicated IP address, email deliverability depends only on you.
- A shared IP address means that several email senders are using the same IP address within one mail server. Email deliverability, in this case, becomes a shared responsibility.
Domain reputation is the reputation of your domain, i.e., the organization you are sending emails from. Even if your IP address changes or you change your mailbox provider, the domain reputation will follow your brand.
Content reputation is about the value of your email copy. It measures how relevant or spammy your email content is.
What is a sender score?
Although a sender score is often mixed with sender reputation, these terms are not the same.
|
A sender score is a number between 0 and 100 that shows the quality of your sender reputation. In other words, it’s the reflection of your sender reputation but in numbers. A sender score is commonly calculated on a rolling 30-day average. |
Why is a sender score important?
It helps you regularly monitor your sender reputation.
How to check your sender score?
You may check your sender score here.
As soon as you register and activate your account, you will be able to enter your IP address or domain and get redirected to the report where you’ll see your sender score.
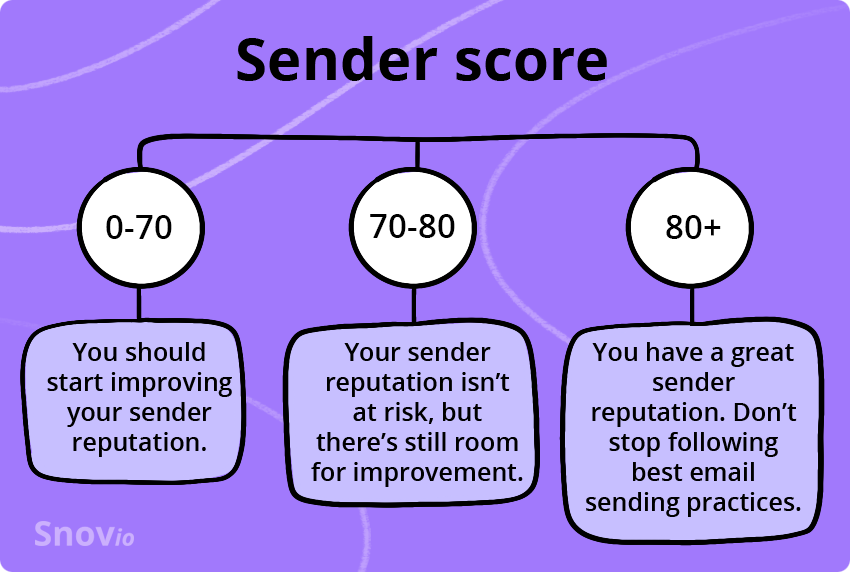
What does my sender score mean?
Overall, the higher your sender score, the higher your chances to reach your subscribers:
But how can you prove to ISPs you are a good sender? With email authentication, of course.
What is email authentication?
|
Email authentication is a technical way of proving that the email address you are sending from belongs to you, and nobody acts on your behalf. |
⚠️You should use email authentication to differentiate yourself from spammers who may send emails from the name of your brand. That may have a detrimental effect on your reputation and your business. ⚠️

13 Best Email Warm-Up Tools (Tested And Compared)
September 19 2023
Email authentication standards
Email authentication relies on three standards: SPF, DKIM, and DMARC:
✔ SPF (Sender Policy Framework) is an email authentication protocol that allows you to define which IP addresses may send emails on behalf of your domain. If the IP address that’s sending on your behalf is listed in the SPF record, then the message passes SPF authentication and vice versa.
✔ DKIM (Domain Keys Identified Mail) provides an encryption key and digital signature that verifies that your email message was not altered by a third party on the way to your subscriber’s inbox.
✔ DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, & Conformance) unites the SPF and DKIM authentication mechanisms into a common framework and defines how the recipient’s mail server should process incoming emails if they don’t pass the authentication check.
You may choose from three types of outcomes:
- p=none: If you set your DMARC policy to p=none, the mailbox provider won’t take any action if your emails fail authentication.
- p=quarantine: Setting your policy to p=quarantine means that emails that fail authentication should be treated suspiciously by mailbox providers and might be sent to the spam or junk folder.
- p=reject: This policy indicates that you want mailbox providers to reject and block all emails that fail DMARC authentication.
Well, it seems pretty difficult to deal with all these standards, but in fact, not so much if you rely on email delivery services that will do email authentication for you. Among such services are SocketLabs, Sendpulse, Kingmailer, and many others.

Email deliverability audit
Checking whether your messages reach your audience will give you the necessary insights to understand how to prevent your emails from landing in the spam folder.
This is where email deliverability audit comes to the rescue!
So what is an email deliverability audit?
|
Email deliverability audit is the assessment of your email outreach campaigns to determine how many emails you’re sending land in your customer’s inbox. |
We recommend performing an email deliverability audit quarterly to keep your finger on the pulse. Meanwhile, it can reveal some problems that need to be handled at once, for example:
- High bounce rate
- High spam rate
- Many unopened emails
- Problems with the quality of your email list, and so on.
How to do an email deliverability audit
Email deliverability audit should be done in several directions:
- Security — your email setup and authentication.
- Reputation — how you send your emails (bounces, spam complaints, etc.).
- Deliverability itself — where your emails go: primary inbox, promotions, or spam.
- Content quality — how well your emails perform: whether they are opened, clicked through or ignored.
Now let’s look at how you may do an effective email deliverability audit.
1. Send a test email
Audit your email service provider and send a test email to see whether it’s placed in the inbox, goes to promotions, or the spam folder. If you are using an email marketing tool, it won’t be difficult. For example, in Snov.io Email Drip Campaigns, there is an option to send a test email after you created one:
As soon as you receive the test email, click “Show original”:
You’ll get an audit report where you can see information on SPF, DKIM, and DMARC:
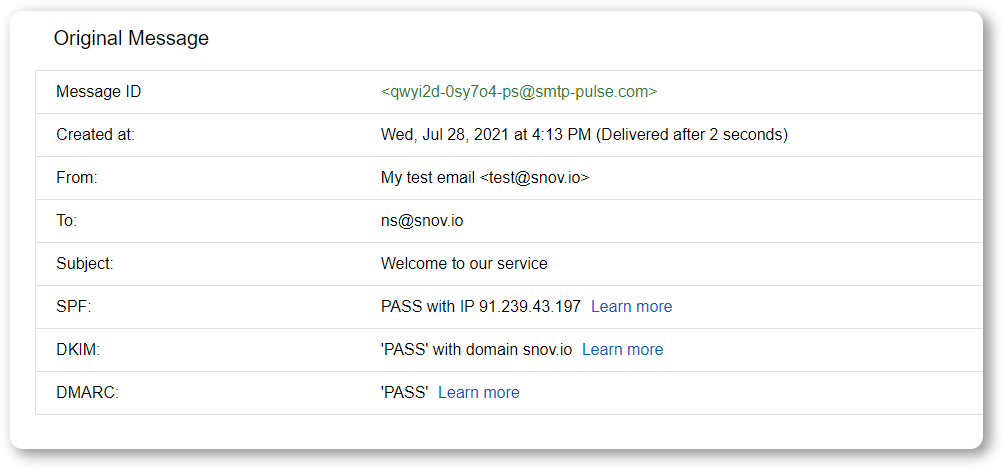
As you can see, this email has passed authentication and found its way into the inbox.
2. Check your code
You may get a deeper analysis of your emails for any red flags by checking the code from the test email you’ve received:
Copy this code into one of the email deliverability tools for analysis, for instance, Mxtoolbox Email Header Analyzer:
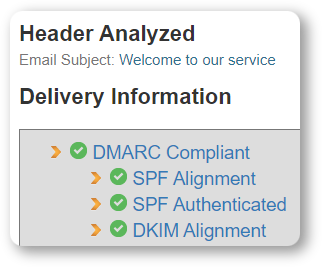
Clicking on each element, you’ll be able to see the extended report.
Alternatively, you may check your email with another email deliverability testing tool — MailTester. It will analyze it in detail (simply click on the drop-down menu) and suggest areas of improvement:
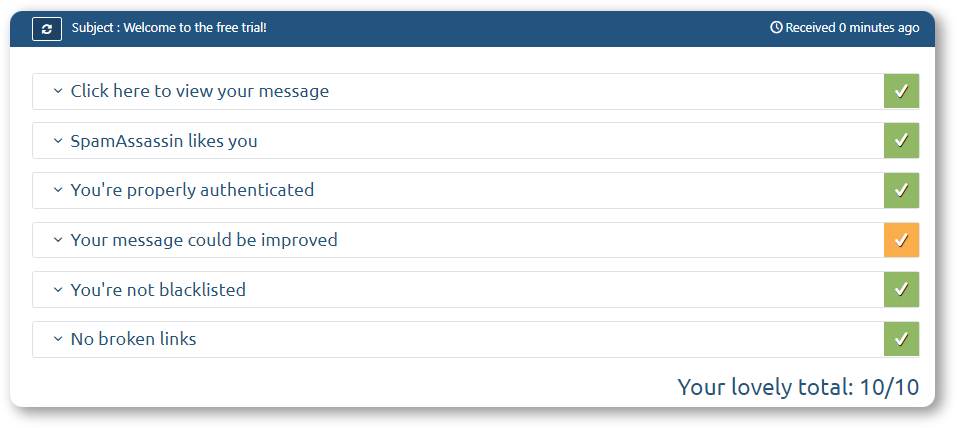
3. Check for blacklisting
Finding yourself on a blacklist is not a joke, as it may be a disaster to your sender reputation. Therefore, don’t forget to check whether you aren’t among the unlucky ones from time to time with the help of Mxtoolbox.
Just like we did:
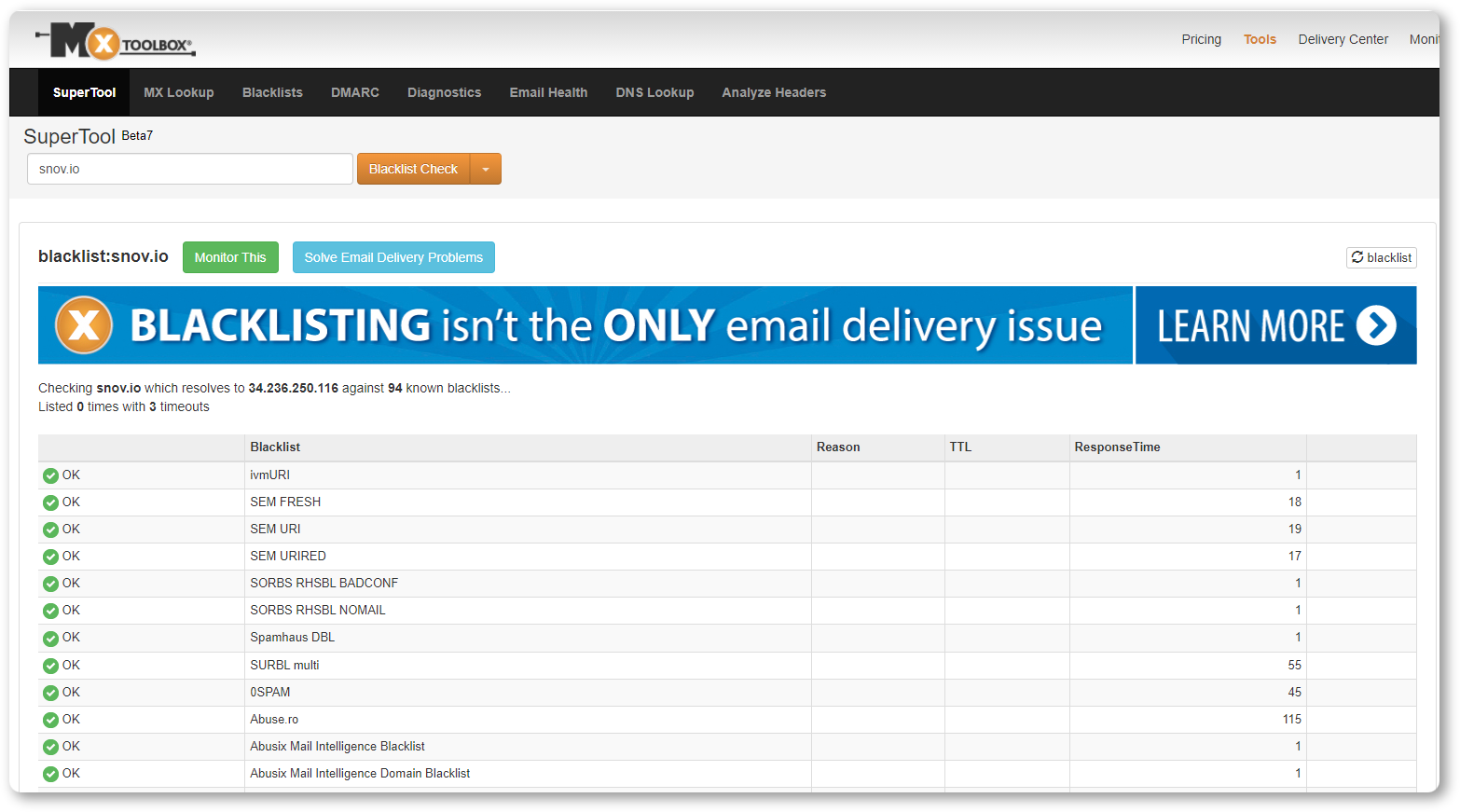
Here I’m just sighing with relief. 🙂
4. Measure your sender score
As mentioned in the previous chapter, the sender score is the mirror of your sender reputation and proof everything is okay with it. Remember to regularly check your sender score (at least quarterly) and work on improving it.
5. Track your customer’s behavior with your emails
It’s important to monitor how your email campaigns perform, but, as a rule, businesses with many users can’t do this manually. They rely on email automation tools that help them see the stats.
For example, Snov.io Email Tracker displays if the receiver has read your email right in your Gmail with a label:
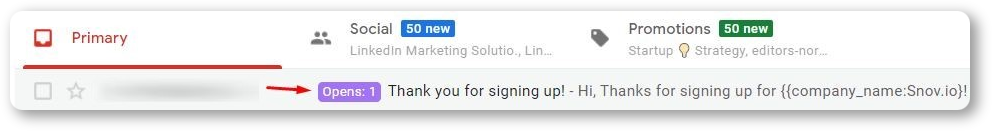
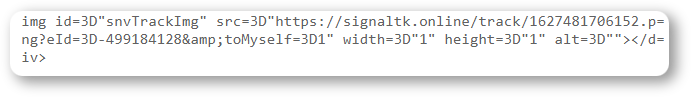
To track your emails, it inserts a tracking pixel you’ll find only in the script:
Email deliverability best practices
Phew, that was a lot of information, wasn’t it? Now, what’s left is learning the tricks of how to place your emails in the inbox of your customers.
1. Warm-up your email account
Warming up your email account is an essential step in the email outreach process as it helps you avoid being flagged as spam. The core issue is to ensure your email is as legitimate and human as possible.
If you are going to use an email automation tool, warm up your email account beforehand. Start with email account personalization by adding a profile picture and an email signature. Further, sign up to social media and other platforms using this email account and join a few mailing lists.
Don’t rush emailing people you don’t know. Write to friends or business partners and ask them to reply to your messages. Respond to their replies. Just make sure your emails don’t look similar and have no spammy words.
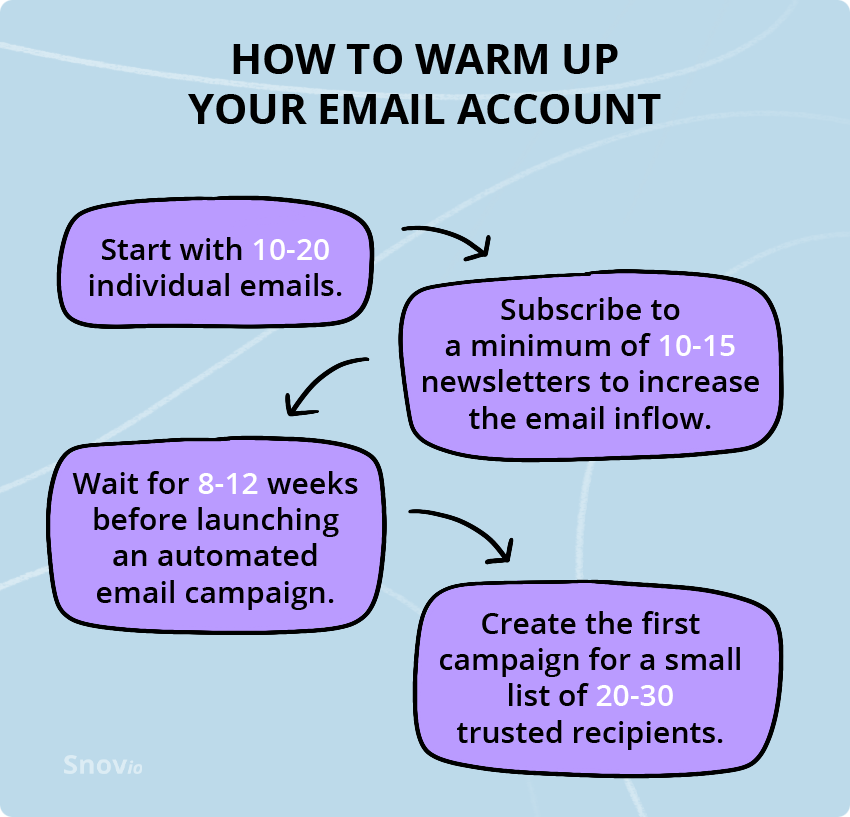
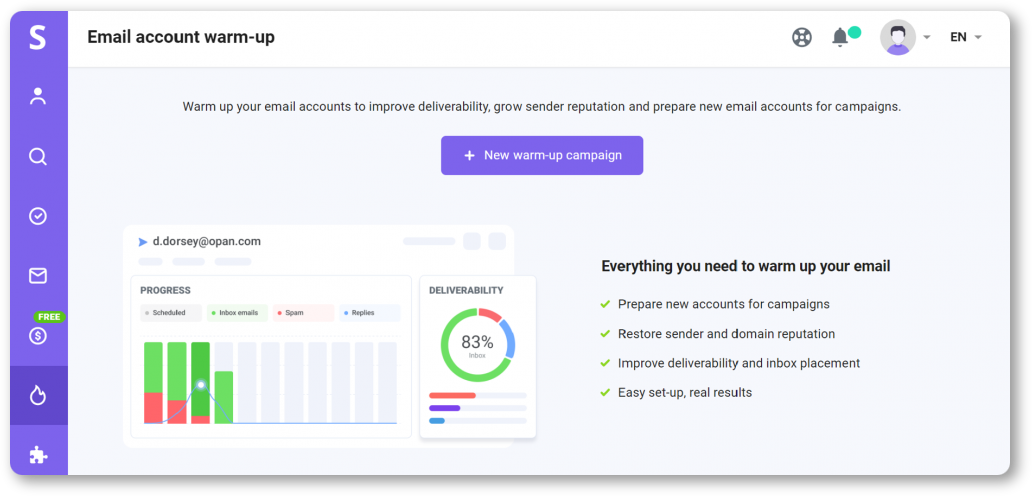
Manual email warm-up is a rather time-consuming process. So if you want to automate it, choose the email warm-up tool that will do everything for you.
For instance, with Snov.io Email Warm-up, you can grow email deliverability right after the first campaign. The tool allows you to choose your purpose of warm-up, set the number of emails that will be automatically sent and replied to, mimicking the real conversation, and ensure your emails won’t land in spam. On top of that, you’ll be able to monitor the warm-up progress status and email deliverability growth.
2. Stay away from purchased email lists
If you think buying an email list will bring you many recipients, I need to disappoint you. The quality of these email addresses won’t be good. And that’s a sure way to spam complaints and poor email deliverability.
Learn more about why purchasing email lists is a bad, bad, bad idea here.
3. Send emails only to people who opted in
To make sure your subscribers are open to your emails, they should give consent to receiving your content. Without it, high chances are you’ll get many unread messages, or worse, they’ll mark your emails as spam.
4. Give explicit options to unsubscribe
People come, people go. Believe it or not, letting them unsubscribe from your emails is much better than crying over poor email deliverability later. You need a quality list, remember? So, give your recipients an explicit option to unsubscribe.
What is more, according to the CAN-SPAM Act (which you should comply with), there must be an unsubscribe link in every email.

5. Segment your email lists
Segmentation is one of the best practices to be followed as it may increase your open rate by 39%. As soon as you’ve built an email list, categorize it according to the types of prospects. This will help you send them only those emails relevant to their needs.
6. Personalize your emails
If segmentation is the queen of email outreach, personalization is by right the king. People love to be addressed personally. And this is not just about calling them by name. Personalization is about demonstrating you care about your subscribers and are ready to give them what they want.
7. Re-engage inactive subscribers
Some of your subscribers don’t react to your emails? Don’t give up, first try to fight a bit more. You may craft re-engagement emails with an exclusive offer to draw their attention to your company. Just think of the power words to catch their eye.
8. Clean your email lists
I also suggest doing a spring cleaning to your email list from time to time and removing recipients who are not replying to your emails and follow-ups. And don’t forget about email validation: do it regularly to avoid keeping invalid email addresses that may bring you undesired bounces.
9. Elaborate on email content
When it comes to email deliverability, much depends on the content of your emails.
About 69% of emails are marked as spam based solely on the subject line. So, ensure your headline isn’t written in all CAPS and doesn’t have any spammy words in it.
As for the email body, try to maintain a 60:40 text-to-image ratio, don’t add too many links, and avoid spam trigger language.
10. Optimize your emails to mobile
With about 6.4 billion smartphone users at the moment, the number of mobile users is going to increase every year. Don’t ignore mobile optimization!
11. Set up your email authentication
Save yourself from any third-party malicious actions on behalf of your email account. Remember to set up email authentication within SPF, DKIM, and DMARC standards to prove you are a real and legitimate sender.
12. Set up a custom tracking domain
If you are using email automation tools, you are sending emails with its custom domain. Google will raise a brow seeing you have your custom domain but keep on sending emails from another one.
Grouping their users across the same domains is a common practice for email automation tools. But if there is a spammer in your group, their fraudulent behavior may damage your deliverability, as your actions will also be associated with spam.
Set up your custom tracking domain to make links in your emails refer to your personal domain instead of the generic one email automation tools use by default.
If you are a Snov.io user, setting up a custom tracking domain won’t be difficult at all: just follow this brief guide.
13. Give preference to dedicated IP
If you send not so many emails, you don’t need to warrant a dedicated IP address. But for a big sender, using a shared IP may be too risky to the email deliverability.
Wrapping up
Finding ways to improve email deliverability is something every email sender has ever puzzled over. There are so many factors that influence the inbox placement of your emails: you should care about security, user engagement, email content, and maintain your high sender reputation whatever happens.
We tried to provide you with an extended guide on what email deliverability consists of and forearmed you with the techniques you may start practicing today to improve it. But there is something I’d like to add: since you most likely will or have already felt the need to automate your processes, much depends on the tool you’ll choose.
Snov.io is a service you can trust. It takes control over spammers, lets you set up your custom tracking domain, provides possibilities for segmentation and personalization, and helps you audit your deliverability.
Not our friend yet? Welcome to your free trial!
Glossary of terms
BCD |
EIP
|
RS |









That’s the best source of information about email deliverability I saw. Great job!
Thanks, Kevin! We’re happy you could find much value in this post.
Special thanks for the glossary. One question about your service. You’ve mentioned there is a warm-up tool in Snov.io. Can I test it somehow?
Yes, of course. You can choose Snov.io Trial plan, which presupposes free warm-up of one account. Learn more about our plans here: https://snov.io/pricing